Most startups embark on their entrepreneurial journey with dreams of success, innovation, and making a significant impact. Yet, the harsh reality is that a significant number of startups fail to survive the challenging early stages. One of the key factors contributing to their demise is the temptation to scale too fast without a solid foundation.
Scaling too fast without a deep understanding of the market and customer needs can be a fatal mistake. It often leads to operational inefficiencies, resource mismanagement, and a misalignment between the company’s offerings and the demands of the target audience. But, by taking a step back and focusing on the foundational aspects of building a startup, entrepreneurs can set themselves up for sustainable growth.
Throughout this blogpost, we will uncover each phase of the startup journey effectively. From the initial exploration and discovery stage to the later stages of exploiting and protecting the business, we will provide actionable strategies to guide you on your path to success.
While the allure of rapid growth may be enticing, we will emphasize the importance of scaling intelligently and validating milestones such as product/market fit. By prioritizing the three most important activities per phase, you can position your startup for sustainable growth and overcome the challenges that often lead to failure.
Join us on this transformative blogpost as we equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the path to long-term growth.
The roadmap to success
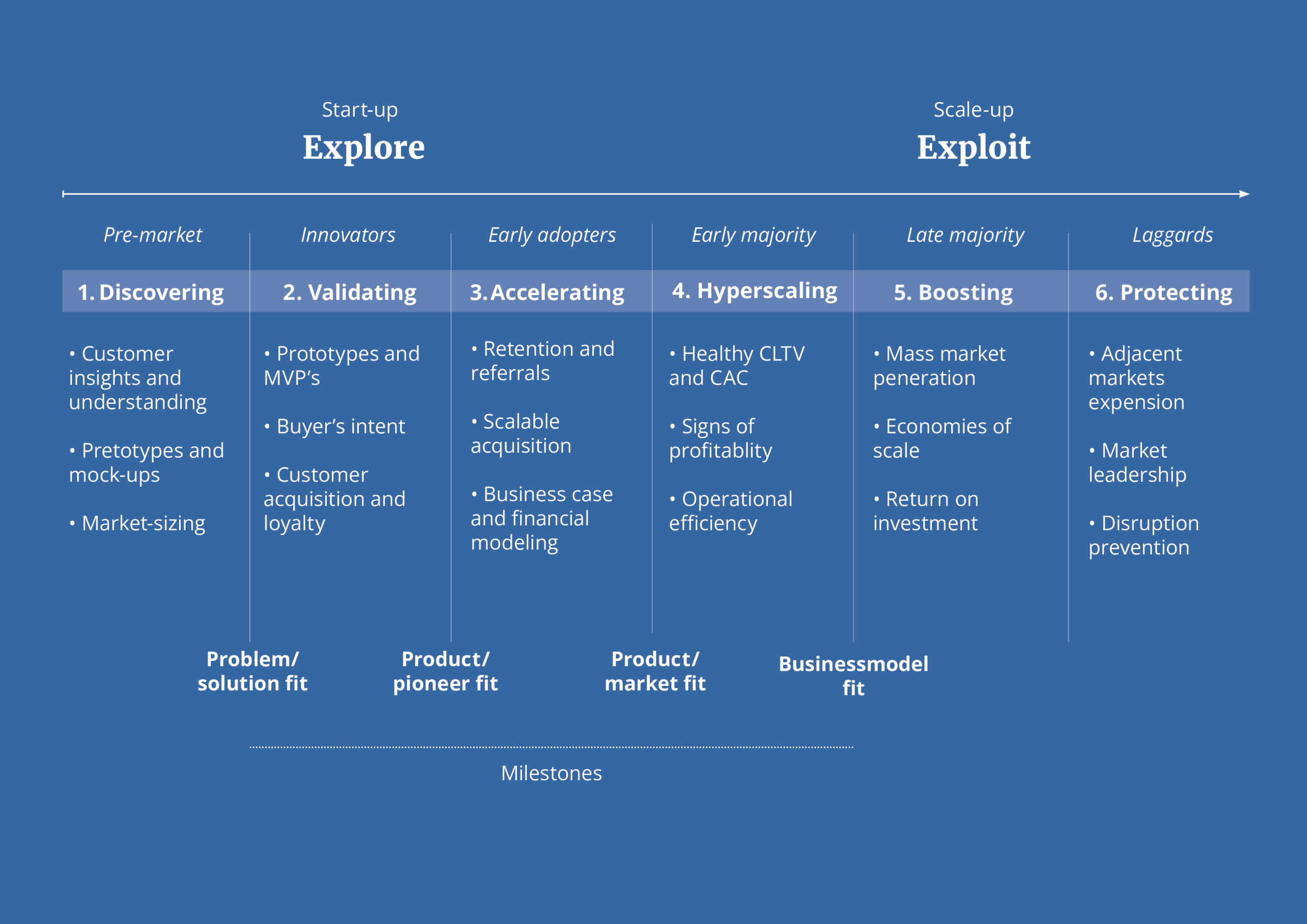
The startup journey can be an exhilarating yet complex endeavor filled with numerous challenges. To navigate this path successfully, entrepreneurs need a roadmap that provides clarity, direction, and a sense of purpose. The roadmap in this blogpost acts as a guiding light, helping startups make informed decisions, prioritize resources effectively, and stay on course towards their goals. It serves as a constant reminder of the big picture, enabling startups to stay focused on their vision while adapting to the dynamic market conditions. Let’s uncover the 6 phases of startup maturity divided into explore and exploit.
Explore vs. Exploit
The explore stage of a startup involves experimentation, validation, and finding product/market fit through iterative learning. In contrast, the exploit stage focuses on scaling and maximizing the value of a proven business model, optimizing operations and driving immense growth.
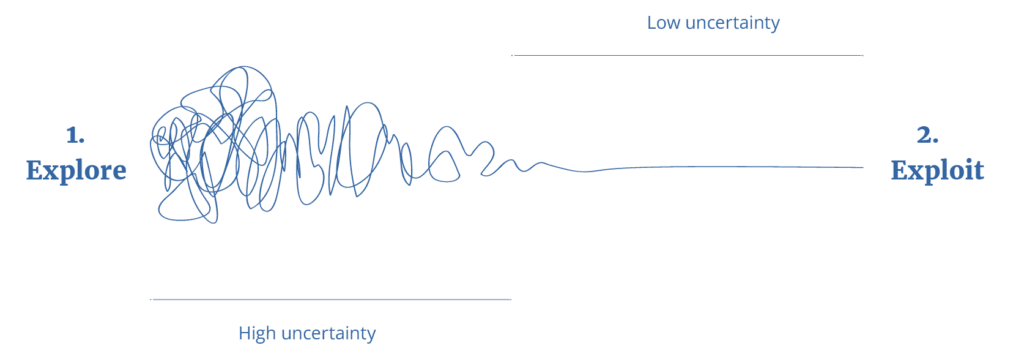
Explore and Exploit in the Adoption Curve
The adoption curve, as proposed by Everett Rogers, represents the rate at which a new innovation is adopted by different segments of the population over time. In the explore stage, the focus is on innovators and early adopters who are open to trying new solutions, while in the exploit stage, the aim is to reach the early and late majority, who require more evidence and social proof before embracing the innovation.
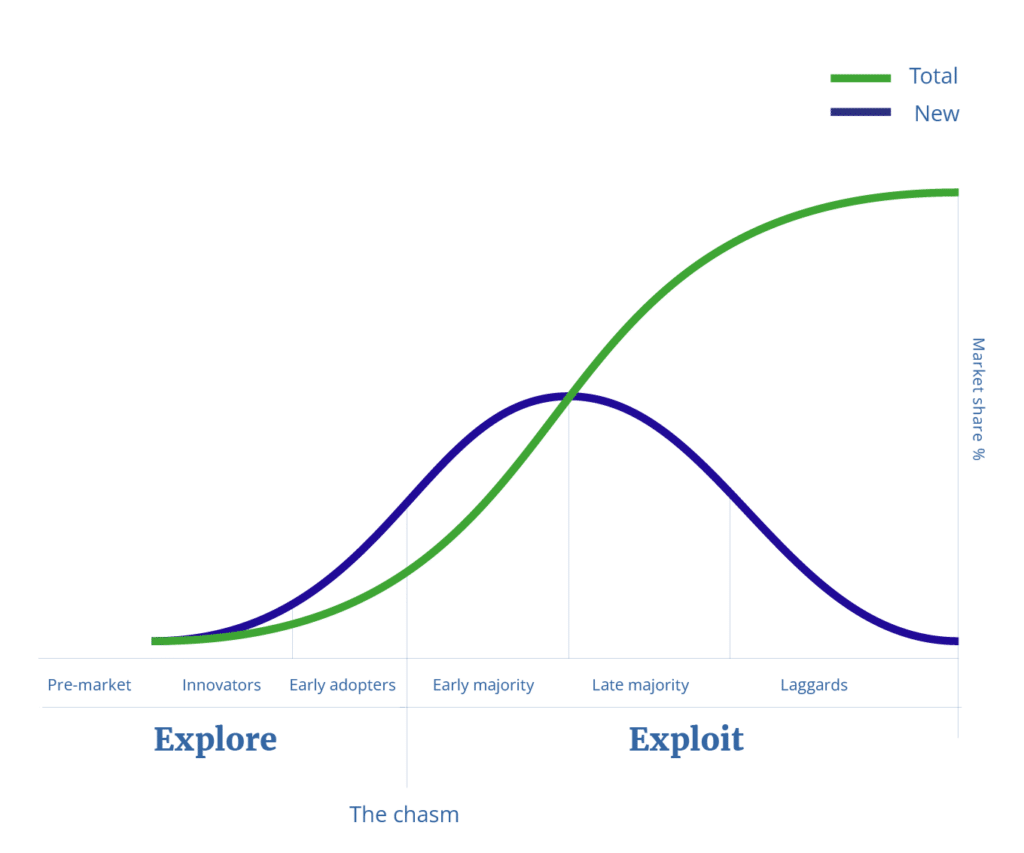
Explore and Exploit divided into 6 phases
Below you will find an image of the 6 startup maturity phases. After that we will discuss all these phases in more detail.
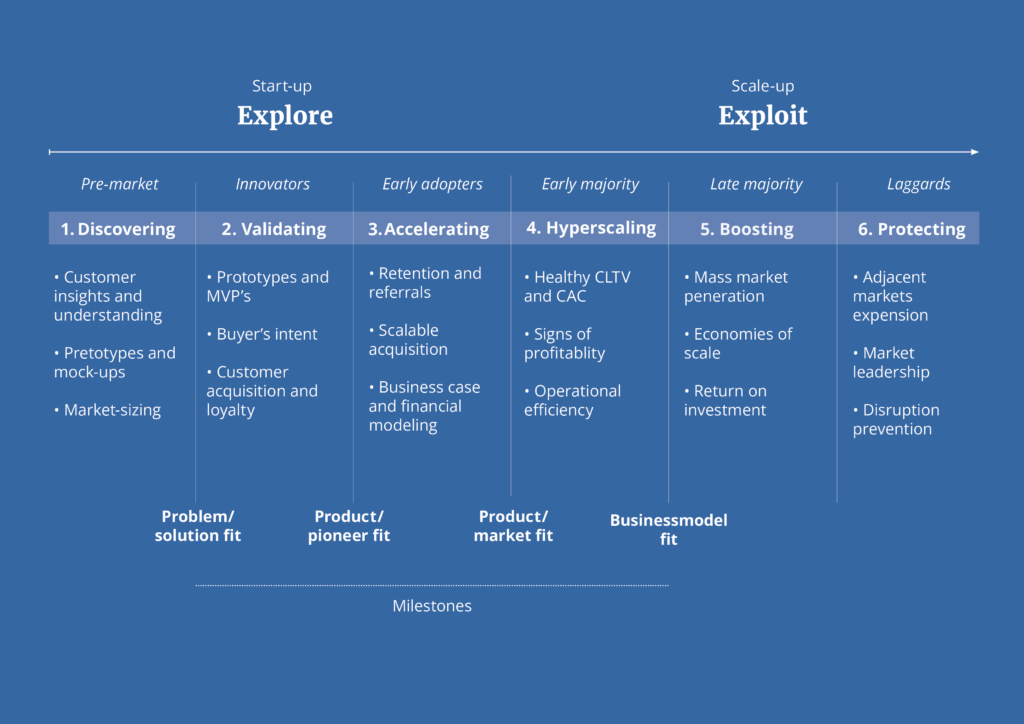
Phase 1: Discovering
Measure customer understanding and context to discover the right solution
In the fast-paced world of startups, the initial phase plays a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of a venture. Phase 1, known as the “Discovering” stage, marks the beginning of the journey, where entrepreneurs embark on a quest to validate their ideas and value propositions.
- Embracing Customer Understanding:
During Phase 1, the focus should be on gaining a deep understanding of the customers and the context in which the venture operates. By validating that customers truly experience the problem and are seeking a solution, entrepreneurs can laythe foundation for future success. Metrics such as the number of potential customers experiencing the problem and their willingness to try the solution become crucial indicators of progress. - Leveraging Pretotyping and Mockups:
Validating the problem/solution fit does not require elaborate technical skills in Phase 1. Entrepreneurs can use various tools like videos, mockups, and pretotypes to convey their ideas and gather feedback. Building a pretotype, a fake version of the product or service, allows entrepreneurs to measure customer behavior through download buttons, pre-orders or sign-up forms. These metrics serve as valuable insights for refining the value proposition and iterating on the solution. - Measuring Market Potential:
Assessing the market potential is critical in Phase 1. Entrepreneurs should focus on identifying the number of potential customers who experience the problem and are willing to try the solution. These metrics provide early indications of market demand and help shape the future growth strategy. It is essential to gauge the market’s size, dynamics, and growth potential to determine the feasibility and scalability of the venture.
Phase 2: Validating
Indicate customers’ willingness to pay and loyalty
As startups progress on their innovation journey, Phase 2, known as the “Validating” stage, becomes the focal point. This critical phase revolves around substantiating the market viability of the venture, solidifying customer interest, and laying the groundwork for future growth.
- Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) / prototype:
As Phase 2 unfolds, entrepreneurs invest efforts in developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). This functional prototype allows for comprehensive testing and validation of the value proposition. By measuring usage and engagement metrics, entrepreneurs gain insights into customer behavior and satisfaction. Iterating on the MVP based on user feedback is crucial to refine the product, enhance its market fit, and generate innovators traction. - Showcasing Customer Willingness to Pay:
In Phase 2, entrepreneurs shift their focus towards demonstrating customers’ willingness to pay for their product or service. The goal is to secure more solid evidence of interest and demand in the market. Entrepreneurs concentrate on acquiring the first sales or obtaining letters of intent for the commercial selling price from potential customers, indicating their commitment to the solution. These metrics, along with customer loyalty measurements, serve as indicators of product/pioneer-fit. - Tracking Customer Acquisition and Loyalty:
To validate the business model further, entrepreneurs need to focus on customer acquisition and loyalty. Metrics such as the number of potential customers who buy the solution and the number of customers using the product extensively after ordering provide valuable insights into market demand and customer loyalty.
Phase 3: Accelerating
Proven the business model on a small scale
Phase 3 of a startup’s journey, known as “Accelerating,” marks a pivotal stage where entrepreneurs focus on scaling their venture and validating the business model on a larger scale. It involves fine-tuning the value proposition, expanding the customer base, and demonstrating the ability to create and deliver customer value efficiently.
- Measuring Customer Retention and Referrals:
In Phase 3, entrepreneurs aim to propel their venture into immense growth by scaling up customer retention and referrals. This involves deploying strategies to attract a large customer base, ensuring custom customer satisfaction and loyalty, and optimizing the delivery of products or services. - Scaling Up Customer Acquisition and Market Reach:
In Phase 3, entrepreneurs shift their attention towards expanding their customer base and reaching a wider market. This involves implementing scalable marketing and sales strategies to attract new customers who fit the product or service. By leveraging marketing channels, partnerships, and targeted campaigns, entrepreneurs aim to increase the number of customers acquired and drive awareness of the venture. - Validating Product/Market Fit with a Minimum Marketable Product (MMP):
At this stage, entrepreneurs seek to solidify the product/market fit by focusing on an extensive working prototype or the first product/service offering. They aim to demonstrate that the value proposition resonates with the target market on a larger scale. Feedback from early adopters and comprehensive customer behavior analysis provide insights into how well the product satisfies customer needs and generates value. By leveraging data-driven insights, and implementing business cases and financial modeling to attract new capital, entrepreneurs create the foundation for hypergrowth.
Phase 4: Hyperscaling
Getting the venture off the ground at a rapid pace
Phase 4 of a startup’s journey, known as “Hyperscaling,” represents a significant turning point where entrepreneurs shift their focus to achieving hypergrowth and building a proven and promising business model. It is a phase characterized by rapid expansion, scaling customer acquisition, and optimizing the delivery of products or services.
- Testing Profitability and Scaling Initiatives:
Phase 4 serves as a critical juncture for testing the venture’s profitability and scaling initiatives. Entrepreneurs seek evidence that supports the expected profitability of the business model when applied on a larger scale. Key metrics such as revenue growth, customer lifetime value (CLTV), and customer acquisition cost (CAC) ratios provide insights into the financial viability of the venture. The focus is on justifying larger investments in customer acquisition and expanding operations. - Focusing on Metrics and Predictable Profitability:
During Phase 4, entrepreneurs shift their attention to key metrics that indicate sustainable growth and predictable profitability. They closely monitor customer lifetime value (CLTV) relative to customer acquisition cost (CAC) while serving the early majority. By optimizing these ratios, entrepreneurs ensure that the venture’s financial performance remains positive and predictable. - Expanding Infrastructure and Human Resources:
Hypergrowth demands a robust infrastructure and sufficient human resources to support the rapid expansion. Entrepreneurs invest in scaling their operational capabilities, including technology infrastructure, logistics, supply chain management, and customer support systems. Additionally, they focus on hiring and retaining top talent, fostering a culture of excellence and innovation within the organization.
Phase 5: Boosting
Strengthening the performance of an established venture
In the journey of a scale-up, phase 5 represents a critical turning point. This phase signifies the venture’s expansion into the broader market, capitalizing on cost advantages through increased volume, and achieving higher returns by optimizing operational processes.
- Penetrating the market:
At this phase, the focus shifts towards reaching the late majority of customers and achieving widespread adoption of the product or service. The goal is to penetrate the mass market by effectively positioning and promoting the offering to a broader customer base. This milestone involves expanding market share, increasing customer acquisition, and maximizing product visibility and awareness. - Using the economies of scale:
As the venture reaches a larger customer base, it can take advantage of economies of scale. This means that the cost per unit decreases as production and distribution volumes increase. By optimizing operations, streamlining processes, and leveraging efficient supply chain management, the venture can achieve cost savings, improved margins, and greater profitability. This milestone is crucial for sustainable growth and competitive advantage. - Higher return on investment (ROI) through operational efficiency:
In this phase, the focus is on maximizing the return on investment by driving operational efficiency across the organization. This involves optimizing resources, reducing waste, improving productivity, and enhancing overall business performance. By fine-tuning processes, automating workflows, and leveraging technology, the venture can achieve higher profitability and financial success. This milestone enables the venture to generate substantial returns while maintaining a strong market position.
Phase 6: Protecting
Achieving market leadership and protect it from disruption
Phase 6 of the startup journey, known as “Protecting,” represents a stage where entrepreneurs focus on maintaining the strength of their established venture and safeguarding it against potential disruptions. It is a phase characterized by efficiency innovation, strategic positioning, and a proactive approach to mitigating risks.
- Maintaining market leadership:
Market leadership signifies the venture’s ability to establish itself as the dominant player in its industry or niche. It involves capturing a significant market share, commanding customer loyalty, and shaping industry trends. Achieving market leadership grants the venture a competitive edge, as it becomes the go-to choice for customers and sets the standards for others to follow. By continuously innovating, delivering exceptional value, and staying ahead of the curve, the venture solidifies its position at the forefront of the market, driving growth, and influencing industry dynamics. - Expending intro adjacent markets:
This milestone involves identifying new market opportunities that are closely related or complementary to the venture’s existing offerings. By leveraging its core competencies, brand reputation, and customer base, the venture can enter these adjacent markets and tap into untapped revenue streams. Expanding into adjacent markets not only diversifies the venture’s portfolio but also reduces reliance on a single market segment, making it more resilient to market fluctuations and expanding its growth potential. It allows the venture to reach new customers, address different needs, and extend its market presence, driving sustainable long-term success. - Preventing disruption:
Disruption prevention is a critical milestone for ventures in the last stage. Disruption can come from various sources, such as emerging technologies, changing customer preferences, or new market entrants. To safeguard its position, the venture must proactively identify potential disruptors, anticipate market shifts, and develop strategies to stay ahead of the curve. This milestone involves continuously monitoring the competitive landscape, investing in research and development, fostering a culture of innovation, and adapting quickly to changes. By actively preventing disruption, the venture ensures its relevance, longevity, and ability to thrive in a dynamic business environment.
FAQs
Q1: What are the key factors contributing to the failure of startups in their early stages?
One of the key factors contributing to the failure of startups in their early stages is scaling too fast without a solid foundation. This leads to operational inefficiencies, resource mismanagement, and a misalignment between the company’s offerings and the demands of the target audience.
Q2: Why is scaling too fast without market understanding a fatal mistake for startups?
Scaling too fast without a deep understanding of the market and customer needs can be a fatal mistake for startups. It often leads to operational inefficiencies, resource mismanagement, and a misalignment between the company’s offerings and the demands of the target audience. This can result in a lack of market traction and ultimately lead to failure.
Q3: What are the six phases of startup maturity?
The six phases of startup maturity are as follows:
- Discovering: Measure customer understanding and context to discover the right solution.
- Validating: Indicate customers’ willingness to pay and loyalty.
- Accelerating: Prove the business model on a small scale.
- Hyperscaling: Get the venture off the ground at a rapid pace.
- Boosting: Strengthen the performance of an established venture.
- Protecting: Achieve market leadership and protect it from disruption.
Q4: How can entrepreneurs validate their ideas and value propositions during the discovering stage?
During the discovering stage, entrepreneurs can validate their ideas and value propositions by gaining a deep understanding of the customers and the context in which the venture operates. They can use tools like videos, mockups, and pretotypes to convey their ideas and gather feedback. Assessing the market potential and identifying the number of potential customers who experience the problem and are willing to try the solution is also crucial.
Q5: What is the importance of achieving market leadership and how can it be maintained?
Achieving market leadership is important as it establishes the venture as the dominant player in its industry or niche. To maintain market leadership, entrepreneurs need to continuously innovate, deliver exceptional value, and stay ahead of the curve. They should monitor the competitive landscape, invest in research and development, foster a culture of innovation, and adapt quickly to changes. By actively preventing disruption, the venture ensures its relevance, longevity, and ability to thrive in a dynamic business environment.
Conclusion
The journey of a startup encompasses six distinct phases, each requiring entrepreneurs to adapt their strategies and approaches. By understanding the unique demands of each phase – from discovering the problem/solution fit to protecting the established venture – entrepreneurs can navigate the challenges and maximize the opportunities presented at each stage. A clear understanding of these phases, combined with strategic decision-making and relentless pursuit of innovation, paves the way for sustainable growth, market leadership, and long-term success in the dynamic landscape of entrepreneurship.